
Although 1820 was more than a generation after the Revolutionary War, British critic Sydney Smith was perhaps still smarting when he wrote in The Edinburgh Review, “In the four quarters of the globe, who reads an American book?” He claimed that the recently independent Americans have “done absolutely nothing…for the Arts, for Literature.” American writers have since been involved in a two-century process of crafting a rejoinder to Smith’s scurrilous assertion. We called this endeavor the “Great American Novel,” and since Smith’s royalist glove-slap the United States has produced scores of potential candidates to that exalted designation. But for all of our tweedy jingoism, the United States seems rare among nations in not having an identifiable and obvious candidate for national epic.
After all, the Greeks have The Iliad and The Odyssey, the Romans have The Aeneid, the Spanish have El Cid, the French The Song of Roland, Italy The Divine Comedy, and the British The Faerie Queene. Even the Finns have The Kalevala, from which our own Henry Wadsworth Longfellow cribbed a distinctive trochaic tetrameter in his attempt to craft an American national epic called The Song of Hiawatha. What follows is a list of other potential American epic poems, where the words “American,” “epic,” and “poem” will all have opportunity to be liberally interpreted. Some of these poems reach the heights of canonicity alongside our ”Great American Novels,” others most emphatically do not. [Editor’s Note: See our “Correction” to this list.]
 The Four Monarchies (1650) by Anne Bradstreet
The Four Monarchies (1650) by Anne Bradstreet
Anne Bradstreet’s collection The Tenth Muse Lately Sprung up in America inaugurated what we could call “American literature.” Scholars have often given short shrift to her so-called “quaternions,” long poems encapsulating literature, history, theology, and science into considerations of concepts grouped in fours (like the four elements, seasons, ages of man, and so on). Her epic The Four Monarchies follows the influence of the Huguenot poet Guillaume de Salluste du Bartas in recounting the historical details of Babylon, Persia, Greece, and Rome, which are commonly associated with the four kingdoms of the biblical book of Daniel’s prophecy. While a committed Protestant (even if her private writings evidence a surprising degree of skepticism), Bradstreet was inheritor to a particular understanding of history that saw the seat of empire moving from kingdoms such as the ones explored in her quaternion, to a final fifth monarchy that would be ruled by Christ. It’s hard not to possibly see a westerly America as the last of these monarchies, as taking part in what John Winthrop famously evoked when he conceived of New England as being a “city on a hill” (incidentally that sermon was delivered aboard the Arbela, which was also transporting Bradstreet and her family to America). Reflecting on that passing from Old World to New, Bradstreet wrote that her “heart rose up” in trepidation, even if she ultimately would come to be the first poet of that New World.
 Paradise Lost (1667) by John Milton
Paradise Lost (1667) by John Milton
Despite John Milton being one of “God’s Englishmen,” Paradise Lost is consummately American in its themes of rebellion, discovery, and the despoiling of paradisiacal realms. The poet’s radical republican politics seemed to prefigure that of the country in the way his native England never could embrace. A century later, in the burgeoning democracy across the Atlantic men like George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, and Ben Franklin read the Milton of the pamphlets Eikonoklastes (which celebrated the execution of Charles I) and Areopagitica (which advocated for freedom of speech) as a prophet of revolution. Scholarship about the poem has often hinged on how Lucifer, he who believes that it is “Better to reign in Hell, than serve in Heaven,” should be understood: as traitor or romantic rebel. For a monarchical society such as England’s, Milton was always more a poet for the radicals than he was one to be celebrated with a monument in the Poet’s Corner. As early Christians once believed Plato and Socrates prefigured Christ, I’ll claim that Milton prefigures America.
The Day of Doom (1662) by Michael Wigglesworth
Milton’s colonial contemporary Michael Wigglesworth has fared less well in terms of posterity, and yet his long apocalyptic poem The Day of Doom stood alongside John Bunyan and the Bible as the most read book in New England well into the 18th and 19th centuries. Wigglesworth epic was the first to fully capture the American public’s obsession with Armageddon (first sacred, now secular), depicting a shortly arriving Judgment Day whereby those who were “Wallowing in all kind of sin” would soon view a “light, which shines more bright/than doth the noonday sun” with the coming of Christ and the destruction (and redemption) of the world. Yet its deceptively simple rhyming couplets about the apocalypse betray an almost ironic, gothic sensibility. A critical edition of the book has yet to be published in our own day, yet the book was so popular that virtually no copies of its first printing survive, having been read so fervently that the books were worn to oblivion.
The Rising Glory of America (1772) by Philip Freneau with Hugh Henry Brackenridge
Four years before the Declaration of Independence was ratified in Philadelphia, the New York born Huguenot poet Philip Freneau stood on the steps of Nassau Hall at Princeton University with his Scottish born classmate Hugh Henry Brackenridge and declared that “here fair freedom shall forever reign.” Six years after that, Freneau found himself held captive for six weeks aboard one of the stinking British prison ships that filled New York Harbor, only to escape and write verse about the ordeal, confirming his unofficial position as the bard of the American Revolution. Those prison ships were notorious at the time, with the bleached skulls and bones of their cast-over victims washing up onto the shores of Long Island, Manhattan, and New Jersey into the early-1800s; as such, Americans thirsted for a soldier-poet like Freneau to embody the republican ideals of independence from British tyranny. Now, two centuries later, the “poet of the American Revolution” is all but unknown, except to specialists. But at the height of his esteem, patriotic Americans, in particular those of a Jeffersonian bent, saw Freneau as an American poet laureate whose verse could extol both the virtues of democratic governance, and the coming prestige of the “Empire of Liberty,” which was to be built upon those precepts. In Freneau’s writings, whether his poetry or his journalistic work for James Madison’s The National Gazette, he envisioned “America” as a type of secular religion, the last act in human history providentially heading towards its glorious conclusion “where time shall introduce/Renowned characters, and glorious works/Of high invention and of wond’rous art.” He may have failed in his goal of being counted among these “Renowned characters,” yet the “wondr’ous art” he predicted to soon arise in this new nation would eventually come to pass.
 Proposed Second Volume (1784) by Phillis Wheatley
Proposed Second Volume (1784) by Phillis Wheatley
We do not know what her real name was. She was kidnapped from her West African home at age seven, and rechristened first “Phillis” after the name of the slave ship that pulled her across the Atlantic, and then “Wheatley” after the pious Boston family who purchased her as chattel. We cannot understand how the Puritan family was able to personally justify ownership of this girl who was translating Horace and Virgil at the age of 12. We do not have record of the hours-long examination she underwent at age 18 with the same number of men (including John Hancock and the Rev. Samuel Mather) to successfully prove herself the author of the volume Poems on Various Subjects, Religious and Moral. The reading public refused to believe that she could have written verse evocative of John Dryden and Alexander Pope without confirmation from those white men who constituted that committee. We cannot tell how genuine her belief is that it “Twas mercy brought me from my Pagan land” as a child on the Middle Passage, where almost a quarter of Africans died before they reached land. We do not know with what intonation she delivered the line “Remember, Christians, Negroes, black as Cain, /May be refin’d, and join th’ angelic train”. We cannot know what may have constituted the conversations between colleagues like the fellow slave Jupiter Hammon, or the Indian poet Samson Occom; we can only read their odes to one another. We do not know how much the shift in her celebrations of George III to George Washington evidence a change in ideology, or the necessary calculus of the survivor. We do not have record of the deprivations she experienced when finally manumitted but forced to work as a scullery maid, or of her husband’s imprisonment in debtor’s prison, or of her pregnancy (her child dying only a few hours after Wheatley herself died at the age of 31). We do not have her second book of poetry, nor its contents. We do not know if this lost epic sits in some sleepy college archive, or is yellowing in a Massachusetts attic, or rebound in some British library. We only know that in her Augustan classicism, her elegant couplets, her poetic voice always forced by circumstance to speak in her oppressors’ tongue, that we are reading one of the finest American poets of the 18th century.
Visions of Columbus (1787) and The Columbiad (1807) by Joel Barlow
In first his Visions of Columbus, and later The Columbiad, Barlow attempted to consciously write an epic befitting his new nation, whose drama he saw as equivalent to that of universal mankind. Borrowing the narrative structure of Paradise Lost, Barlow envisions a westerly angel named Hesperus as appearing to Christopher Columbus in a Castilian prison cell and revealing the future epic history of the continents he (supposedly) discovered. In The Columbiad Barlow wished to “teach all men where all their interest lies, /How rulers may be just and nations wise:/Strong in thy strength I bend no suppliant knee, /Invoke no miracle, no Muse but thee.” Columbus may have been a strange heroic subject for the eventually steadfastly secular Barlow, but in the mariner the poet saw not the medieval minded Catholic zealot of historical reality, but rather a non-English citizen of Renaissance republicanism (and thus an appropriate patron for these new lands). Barlow’s contemporary Percy Shelley famously wrote that poets are the unacknowledged legislators of the world; in Barlow’s case language, whether poetic or diplomatic, was central in the project of constructing these new men of the New World. Barlow had long rejected the religion of his youth, and saw in the United States a new, almost millennial nation, which would fulfill humanity’s natural inclination towards freedom, where “that rare union, Liberty and Laws, /Speaks to the reas’ning race ‘to/freedom rise, /Like them be equal, and like them be/wise.”
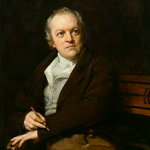 America: A Prophecy (1793) by William Blake
America: A Prophecy (1793) by William Blake
Already critiqued as turgid in its own day, Barlow’s The Columbiad has only become more obscure in the intervening two centuries. Yet what it loses in number of overall readers, the poem makes up for it in the genius of those who were inspired by it, with that mystic of Lambeth William Blake reading Barlow and penning his own America: A Prophecy in visionary emulation of it. Blake is deservedly remembered as a poetic genius, Barlow not so much. The non-conformist eccentric genius “looking westward trembles at the vision,” saw in the rebellion of “Washington, Franklin, [and] Paine” the redemption of all mankind. Inspired by a heterodox religious upbringing, the rich poetic tradition of England, the coming fires of Romanticism, and the particular madness and brilliance of his own soul, Blake composed the most emancipatory verse of his or any era. With his vocation to break the “mind forg’d manacles” which enslave all mankind, Blake saw the great 18th-century revolutions in America and France as not just political acts, but indeed as ruptures in the very metaphysical substance of reality. The narrative is typical Blake, encoded in a biblical language so personal that it remains inscrutable as it is beautiful. The angel Orc, rebelling against the anti-Christ surrogate Albion, prophecies that “The morning comes, the night decays, the watchmen leave their stations/The grave is burst, the spices shed, the linen wrapped up.” In a rejection of his servitude, this spirit of independence declaims, “no more I follow, no more obedience pay.” An Englishman writing in England with a heart more American than any of the revolutionaries he celebrates, Blake writes, “Then had America been lost, o’erwhelmed by the Atlantic, /And Earth had lost another portion of the Infinite;/But all rush together in the night in wrath and raging fire.” But Blake’s hatred of all kings was consistent, he rejected the idolatrous apotheosis of the god-president Washington, and as is the fate of all revolutionaries, America would ultimately break his heart. For Blake, no nation proclaiming liberty while holding so many of its people in bondage could claim to be truly independent. Freedom was still to be found elsewhere.
 Madoc (1805) by Robert Southey
Madoc (1805) by Robert Southey
Because his and his friend Samuel Coleridge’s dreams of founding a utopia on the Susquehanna River would be unrealized, Southey’s American dreams remained in England, where he composed an unlikely epic charting a counterfactual history imagining epic battles between the Welsh and the Aztecs. The poem is based on legends surrounding the Welsh prince Madoc, who in the 12th century supposedly escaped civil war in his home country to travel west and dwell among the Indians of America. There is an enduring quality to these sorts of apocryphal stories of pre-Colombian trans-Atlantic contact. The Elizabethan astrologer John Dee used these legends as justification for English colonization of the Americas, explorers ranging from Spanish conquistadors to Jamestown natives claimed to have found blonde-haired Welsh speaking Indians, and in Alabama and Georgia historical markers reporting these myths as facts stood as recently as 2015. The undeniable excitement and romance of such a possibility is threaded throughout Madoc, which pits Celt against Aztec and druid against pyramid high-priest, with a council of Welsh bards naming the prince a “Merlin” to the Americas. The poem is ready-made for the cinematic treatment, even as its imaginary medieval battles allowed the once idealistic Southey to overlook the unequal violence of historical colonialism, and in the process to embrace an increasingly conservative politics. Yet the Arthurian fantasy of the story is inescapably fascinating, as Southey asks, “Will ye believe/The wonders of the ocean? how its shoals/Sprang from the wave, like flashing light…/language cannot paint/Their splendid tints!”
 The Song of Hiawatha (1855) by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
The Song of Hiawatha (1855) by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
Once Henry Wadsworth Longfellow was the greatest American bard, the most accomplished of the Fireside Poets, whose verse celebrated Yankee independence and liberty. The question of what America’s national epic was would be easy for a good Victorian — it could be nothing other than Longfellow’s The Song of Hiawatha. And yet the literary critical history of the 20th-century was not kind to the bearded old New Englander. The degradation has become such that current poet Lewis Putnam Turco derides Longfellow as “minor and derivative in every way… nothing more than a hack imitator.” In the years and decades after its composition, generations of American school-children memorized the opening lines of Longfellow’s poem: “On the shores of Gitche Gumee, /Of the shining Big-Sea Water, /Stood Nokomis, the old woman, /Pointing with her finger westward,/O’er the water pointing westward,/To the purple clouds of sunset.” The distinctive trochaic trimeter, borrowed from the Finnish epic The Kalevala gives the epic a distinct beat intentionally evoking an Indian pow-wow as imagined by Longfellow. Critical history has not only been unkind to Longfellow, it has also been unfair. While Freneau and Barlow consciously mimicked European precedents, and Southey constructed his own imaginary representations of the Aztec, Longfellow tried to tell an indigenous story as accurately as he could (even if his own identity may have precluded that as a possibility). Based on his friendship with the Ojibwa chief Kah-Ge-Ga-Gah-Bowh and the Sauk chief Black Hawk, the poet attempted to use indigenous history and religion to craft a uniquely American epic. For much of its reception history American readers took the poem as precisely that. Longfellow’s tale sung of Hiawatha, a follower of the 12th-century Great Peacemaker of the Iroquoian Confederacy who preached in the western hills around Lake Superior and of New York and Pennsylvania. Though little read anymore, the poem still echoes as an attempt not just to write an epic for America, but also to transcribe a genuinely American epic.

 “Song of Myself” (1855) by Walt Whitman
“Song of Myself” (1855) by Walt Whitman
Both The Song of Hiawatha and “Song of Myself” were published in 1855; and while the former sold 50,000 copies upon release, Walt Whitman’s Leaves of Grass, self-published in a Brooklyn print shop, didn’t even sell out its small initial run of 800. Of the few reviews published, most seemed to repeat some variation of the critic who called the slender volume “reckless and indecent.” And yet a century and a half later it is Whitman whom we hold in the highest esteem, as America’s answer to Milton or Blake. For in Whitman we have the first genuine rupture in American literary history, with the New York poet following Milton’s lead in “things unattempted yet in prose or rhyme.” For Whitman abandoned the conventional rules of prosody, loosening tongue and ligament to craft a lusty and hearty free verse equal parts Bowery dock-worker and King James Bible. So what, exactly, was Whitman’s epic about? In short, it took as its subject — simply everything. The poem is about the “marriage of the trapper in the open air in the far west,” and “The runaway slave” who came to a house and “stopt outside,” and also “The young men” who “float on their backs” whose “white bellies bulge to the sun,” and “The pure contralto” who “sings in the organ loft,” and “The quadroon girl” who is “sold at the auction stand” and “The machinist” who “rolls up his sleeves,” as well as “The groups of newly-come immigrants.” He understood that in a truly democratic society the Golden Age platitudes of the traditional epic form could not truly confront the vibrant, egalitarian reality of lived experience, and so rather than sing of Columbus, or Washington, or Hiawatha, Whitman asks us to “celebrate yourself.” The “I” of “Song of Myself” is not quite reducible to Whitman as the author, and therein lies the genius of his narration, for he elevates himself in a sort of literary kenosis, becoming an almost omniscient figure for whom the first-person personal pronoun comes to almost pantheistically encompass all of reality. And though Whitman was a type of mystic, he was always consciously American as well, penning that most American of genres — advertisements for himself.
 Complete Poems (c.1886) by Emily Dickinson
Complete Poems (c.1886) by Emily Dickinson
Dickinson is not the author of any conventional epic, nor would she have considered herself to be an epic poet. What she offers instead are close to 2,000 lyrics, so finely and ingeniously structured, so elegant in the relationship between line and image and rhythm, that taken as a whole they offer a portrait of a human mind anticipating death that is as consummate and perfect as any offered by any other poet. Like Leaves of Grass, the fragments of Dickinson scribbled on the backs of envelopes and scraps of paper present an epic that is secretly, yet simply, the reader’s own life story. Dickinson belongs among that collection of the greatest philosophers, whose orientation towards truth is such that she is able to tell us that which we all know, but were unable to say. Take the line “I am Nobody! Who are you? /Are you – Nobody – too?” With her characteristic idiosyncratic punctuation (that capitalized “Nobody!”) and the strange, almost-ironic interrogative declaration. In her logical statement of identity, which is built upon negation, she offered a Yankee version of God’s declaration in Exodus that “I am what I am.”
 The Cantos (c.1915-62) by Ezra Pound
The Cantos (c.1915-62) by Ezra Pound
His Cantos are the strangest epic, a syncretic alchemy of American history, Chinese philosophy, and ancient Greek poetry. Almost impenetrable in their hermeticism, Pound’s actual phrases were able to distill the essence of an image to their very form. Yet he was also an anti-American traitor, madman, war criminal, propagandist, and defender of the worst evils of the 20th century. He was an ugly man, but as a poet he could cut excess down to crystalline perfection: “The apparition of these faces in the/crowd;/Petals on a wet, black bough.” Some 20 years after his infamous wartime broadcasts for the Italian fascists, a faded, broken, wrinkled, and ancient Pound found himself living in Venice. Sitting before the elderly man in that Venetian villa was a balding, magnificently bearded Allen Ginsberg, the Beat poet and Jewish Buddhist, there to break bread with Pound. Ginsberg brought along some vinyl to play; he wished to demonstrate to Pound the distinct American speech that threaded from the older poet through Ginsberg and to that other Jewish folk troubadour, this one named Robert Allen Zimmerman. The younger poet, reportedly forgiving and gracious to a fault, claimed that Pound apologized for his anti-Semitic betrayals during the war. Yet this was not an act of contrition — it was a request for cheap grace. Beautiful verse can sprout from poisoned soil. We can still read him, but that does not mean that we need to forgive him, even if Ginsberg could.
 John Brown’s Body (1922) by Stephen Vincent Benét
John Brown’s Body (1922) by Stephen Vincent Benét
The writer from Bethlehem, Penn., attempted his classically structured epic poem at an unfortunate cultural moment for classically structured epic poems. Though it won a Pulitzer Prize a year after it was written, John Brown’s Body remains largely forgotten. Though Benét’s conservative aesthetics that call upon the “American muse, whose strong and diverse heart/So many have tried to understand” may seem retrograde, what’s actually contained is the fullest poetic expression of the definitional moment of American history. John Brown’s Body, which teaches us that “Sometimes there comes a crack in Time itself,” returns to slavery, the original sin of American history, and to the incomplete war waged to bring an end to the horrors of bondage. Benét, most famous for his story “The Devil and Daniel Webster” (which if anything has reached the level of fable, its author’s name largely forgotten) attempted to craft an epic to commemorate the Civil War while its veterans still lived. His task is conscious, perhaps thinking of Barlow, Freneau, and others, he writes of his nation “They tried to fit you with an English song/And clip your speech into the English tale. /But, even from the first, the words went wrong.” The poem would be mere affectation if not for how beautiful lines of the poem could be, and if not for how important the poet’s task was, and if not for just how often he comes close to accomplishing it.
 The Bridge (1930) by Hart Crane
The Bridge (1930) by Hart Crane
From his apartment at 110 Columbia Heights the poet Hart Crane could see that massive structure that began to span from Brooklyn into lower Manhattan. Like Barlow, Crane borrows the character of Columbus, as well as other semi-mythic American personages such as Pocahontas and Rip Van Winkle in leading up to his own experience of seeing this new wonder of the world unite two formerly separate cities. Beneath the shadow of the bridge he asks, “How many dawns, chill from his rippling rest/The seagull’s wings shall dip and pivot him, /Shedding white rings of tumult, building high/Over the chained bay waters Liberty.” The poem was written as a rejoinder to the pessimism in that other epic, T.S. Eliot’s The Waste Land. Crane’s own life could be desperate: alcoholic and dead at 32 from his own hand after being savagely beaten by a homophobic crowd. Yet in The Bridge he tries to marshal that definitional American optimism, this sense of a New World being a place that can make new people. A contemporary critic noted that the poem, in “its central intention, to give to America a myth embodying a creed which may sustain us somewhat as Christianity has done in the past, the poem fails.” And yet whether this is said fairly or not, it misses the point that all epics must in some sense be defined by failure, the only question is how well you failed. By this criterion, in its scope, breadth, ambition, and empathy, Crane failed very well.
 “Middle Passage” (c.1940) by Robert Hayden
“Middle Passage” (c.1940) by Robert Hayden
Benét intuited that slavery was the dark core of what defined this nation, and that no understanding of who we could be can ever really begin till we have fully admitted to ourselves what we have been. The poet Robert Hayden concurred withBenét, and his “Middle Passage” was a black expression of the horrors and traumas that defined American power and wealth, a moral inventory that explicates the debt of blood owed to the millions of men, women, and children subjugated under an evil system. His epic is one of the fullest poetic expressions of the massive holocaust of Africans ripped from their homes and transported on the floating hells that were the slave ships of the middle passage, telling the narrative of “Middle Passage:/voyage through death/to life upon these shores.” No complete personal memoir of the middle passage survives (with the possible exception of 1789’s The Interesting Narrative of Olaudah Equiano) and so Hayden had to make himself a medium or a conduit for voices that were silenced by the horrors of slavery, writing of “Shuttles in the rocking loom of history, /the dark ships move, the dark ships move.” Hayden had certainly never been in the stomach of a slave ship himself, and yet he conveys the knowledge that “there was hardly room ‘tween-decks for half/the sweltering cattle stowed spoon-fashion there;/that some went mad of thirst and tore their flesh/and sucked the blood.” “Middle Passage” is such a consummate American epic precisely because it enacts the central tragedy of our history, but its ending is triumphant, depicting the emergence of a new hybridized identity, that of the African-American. The conclusion of Hayden’s poem is inescapable: all that is most innovative about American culture from our music to our food to our vernacular to our literature has its origins in the peoples who were brutally forced to this land.
 Paterson (1946-63) by William Carlos Williams
Paterson (1946-63) by William Carlos Williams
Of course a town like Paterson, N.J., could generate an epic five-volume poem, penned by her native son, the pediatrician-bard William Carlos Williams. True to his Yankee ethic, Williams’s philosophy was one that was vehemently materialist, practical in its physicality and imploring us to “Say it! No ideas but in things.” In Paterson Williams’s answered Eliot’s obscure Waste Land with a poetic rejoinder, one that rejected the later poet’s obscurity and difficult language with a paean to the lusty American vernacular every bit the equal of Williams’s fellow New Jerseyite Whitman. That language flowed as surely as the Passaic River across those five volumes, and over two decades of writing. What the poem provides is a thorough and deep history of this particular place, using it as a reflective monad to encompass the history of the entire country from colonialism, through revolution and industrialization into the modern day. In Williams’s epic the reader experiences, “The past above, the future below/and the present pouring down: the roar, /the roar of the present, a speech –/ is, of necessity, my sole concern.”
 Howl (1955) by Allen Ginsberg
Howl (1955) by Allen Ginsberg
The Blakean New Jerseyite may have implored us to topple Moloch’s statue, but we used his poem to sell coffee, jeans, and computers. A criticism of the Beats was always that their modus operandi was more style than substance, a disservice to Howl, which when read free of the accumulated cultural debris that surrounds it is still thrillingly inspired. “I saw the best minds of my generation destroyed by madness, starving, hysterical, naked” (at a tender age I inscribed those very lines around the white edge of a pair of black Converse hi-tops with a purple felt pen). Howl can seem a mere product of the mid-century counterculture, but that doesn’t mean that his bop Kabbalistic vision of the sacred embedded within the grit and muck of marginalized people — the radials, and junkies, and queers, and addicts, and drunks — doesn’t remain profoundly beautiful. Ginsberg sings the song of “Angel-headed hipsters burning for the ancient heavenly connection/to the starry dynamo in the machinery of night.” Dedicated to one of these lost children of America, Carl Solomon, who Ginsberg met in a Patterson mental hospital, Howl’s vision is profoundly redemptive, despite its depiction of an America that is more Babylon than “City on a hill.”
 The Battlefield Where the Moon Says I Love You (1972) by Frank Stanford
The Battlefield Where the Moon Says I Love You (1972) by Frank Stanford
The poet Frank Stanford marshaled that Southern history that hangs as thick as a blanket of lightning bugs on a humid July night in his brilliant The Battlefield Where the Moon Says I Love You. If not America’s great epic than it is surely the South’s, where the poem is all moonshine and Elvis Presley, yet not reducible to its constituent parts. Following the lead of modernists like E.E. Cummings, Stanford produced a massive poem devoid of punctuation and reproduced without any stanzas, one that never reached the heights of canonicity despite being celebrated by poets like Alan Dugan as among the greatest American works of the 20th century. The Battlefield Where the Moon Says I Love You endures as a half-remembered phantom born out of a particular Southern dark genius, and now almost folk-myth as much as it is actual text, out of print for years at a time. Stanford, who killed himself with three pistol shots to the chest at the age of 30 in 1978 endures as a literary ghost, still searching for a deserving audience. As he wrote, “Death is a good word. /It often returns/When it is very/Dark outside and hot, /Like a fisherman/Over the limit, /Without pain, sex, /Or melancholy. /Young as I am, I/Hold light for this boat.”
 The New World (1985) by Frederick Turner
The New World (1985) by Frederick Turner
Perhaps a central anxiety of American literature, which reflects on the endlessly novel and regenerative possibilities of this Golden Land, is that as the clock ticks forward we become less and less new. Hence the necessity to continually reinvent, to “make it new” as Pound put it. The Neo-Formalist poet Frederick Turner takes this injunction very literally with his provocative science fiction epic appropriately titled The New World. Set in a fantastic 24th century, Turner envisions a fractured and disunited states of America born out of the fissures and inconsistencies that always defined American cultural identity. There are now groups like the anarchic Riots, the Eloi-like Burbs, the theocratic Mad Counties, and the Jeffersonian Free Counties. What follows is an archetypal story of family feuding, exile, and messianism across these designated polities, and in the process Turner tells a narrative about America’s history by imagining America’s future. Invoking the muse, as is the nature of the epic convention, Turner writes “I sing of what it is to be a man and a woman in our time.” What follows is a circus-mirror reflection of America, brilliantly harnessing the potential of science fiction as a modern genre and using the vehicle of the seemingly moribund epic form to sing a new story. The future setting of Turner’s epic serves to remind us that this mode, so much older than America, will also outlive us.
 The Forage House (2013) by Tess Taylor
The Forage House (2013) by Tess Taylor
As genealogy-obsessed as we may be, many Americans have an anxiety about fully recognizing their own reflections in past mirrors, with the full implications of where we’ve come from steadfastly avoided. Poet Tess Taylor writes, “At first among certain shadows/you felt forbidden to ask whose they were.” In The Forage House she crafts an American epic by writing a personal one; she interrogates the long-dead members of her own lineage, pruning the tendrils of her family tree and discovering that while genealogy need not be destiny, it also must be acknowledged. A native Californian, she is descended from both New England missionaries and Virginian slave owners, with one ancestor in particular, Thomas Jefferson, as enigmatic a cipher as any for the strange contradictions of this land. Jefferson may not have admitted that branch of his family tree sired through his slave Sally Hemings, but Taylor seeks out her black cousins. To do this isn’t an issue of political expedience, but one profoundly and necessarily urgent in its spiritual importance. Perhaps it is in the collection of people that constitute a family, and indeed a nation, where we can identify an epic worthy of the nation. Rugged individualism be damned, we’re ultimately not a nation of soloists, but a choir.
 Citizen: An American Lyric (2014) by Claudia Rankine
Citizen: An American Lyric (2014) by Claudia Rankine
The dark irony of the word “citizen” as the title of Rankine’s poem is that this postmodern epic explores the precise ways that this nation has never treated its citizens equally. Combining poetry, creative nonfiction, and a stunningly designed image, Citizen has the appearance of a photography magazine but the impact of a manifesto. The cover of the book depicts a gray hood, isolated in a field of white, presented as if it were some sort of decontextualized object or museum piece. But the hoodie calls to mind the murdered Florida teenager Trayvon Martin; Citizen ensures that we can never view an artifact as this out of context. The awareness that Citizen conveys is that this is a nation in which a black child like Martin, simply walking home from the store with iced tea and Skittles, can be killed by an armed vigilante who is then acquitted by a jury of his peers. But it would be a mistake to think that Rankine’s poem is some sort of sociological study, for as helpful as the adoption of terms like “privilege” and “intersectionality” have been in providing a means for political analysis, Citizen displays the deep, intuitive wisdom that only poetry can deliver — racism not simply as a problem of policy, but also as a national spiritual malady. From Frederick Douglass’s “What to the Slave is the Fourth of July?” to Citizen, conservative critics have purposefully obscured the purposes of these poetic sermons. Yet what Rankine attempts is profoundly American, for Citizen conveys that any America falling short of its stated promises is an America that betrays its citizens. As she writes, “Just getting along shouldn’t be an ambition.” In answering what our national epic is, Uncle Walt said that “The United States themselves are essentially the greatest poem;” the importance of Citizen is that it reminds us that this poem has yet to be fully written.
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons.









